When it comes to skincare, understanding the role of light can be very confusing. Ordinarily the two topics may even feel unrelated. However, with the use of light therapy becoming increasingly popular, you might be asking yourself questions like, Do acne light therapy devices even work? Is LED light therapy the same as exposing yourself to the sun? And if so, Isn’t exposure to sunlight bad for your skin? How and when do I know which light is good or bad for my skin?
The answers are yes, yes, and allow me to explain. Here, we’ll be covering all the fundamentals of the role of light on your skin and how you can utilize your knowledge to get clearer, healthier skin.
1. What are the different types of light?
2. How does sunlight affect your skin?
3. How does LED light affect your skin?
What are the different types of light?
We’re going to start with a mini-physics lesson on light. Don’t leave yet! I promise it will be fast(and it will be useful).
A few basics on what’s relevant:
1. There are different types of light
2. While there are a number of factors that differentiate one light from another - a primary one is wavelength
3. Wavelength is measured in nanometers (or nm for short).
3. The shorter the wavelength, the higher the frequency (and the tighter the structure of the wave)
Now, back to skincare. Different wavelengths penetrate the skin to different extents- that’s the key to understanding light to skincare. Here is a quick breakdown of the different types of light we will discuss today.
| Sunlight ☀️ | Visible Light 💡 | |||
| UVC | UVB | UVA | Blue | Red |
| 100-280nm | 280-315nm | 315-400nm | 400-500nm | 620-700nm |
In this article, we’ll be discussing the key differences between different types of light. Whether you are someone who applies sunscreen religiously every day or believes that you can heal your acne with the sun, the key to understanding if the light is right for you or not is to understand the properties of light.
How are acne light therapy devices different from sunlight?
Sunlight is made up of 53% infrared, 43% visible, and 4% higher energy UV light. Here, as our biggest
There are generally three types of UV lights: UVA, UVB, and UVC light. Each of them have a different impact on the skin.
UVC : UVC rays are the most dangerous among the three. UVC radiation can cause severe burns and eye injuries. However, because it is unable to penetrate so deep into the skin it is unlikely to cause skin cancer, cataracts, or permanent loss of vision. Thankfully, UVC rays from the sun are absorbed by the ozone layer and pose little threat to humans.
UVB: UVB radiation has a longer wavelength than UVC and is able to cause a lot more damage. It penetrates and damages the outermost layer of the skin-causing sunburns and blistering. UVB penetrates penetrates into the, with enough UVA rays and damage the DNA. The DNA can repair itself but with enough exposure, it will eventually damage your skin. It can be blocked by sun
While 90% of the UVB is absorbed by the ozone, the 10% still causes a significant amount of damage. While the UVB intensity fluctuates on the weather, time of day, and location, we can protect ourselves against it with sunscreen or glass windows.
UVA: UVA is the final radiation we should discuss. It is able to penetrate deeper into the skin and usually causes tanning. One thing to understand is that there is no such things as a safe/healthy tan (no matter how good it may look). In fact, tanning is your body producing more melanin as a defense mechanism when it expects to be exposed to the sun. Sun burns is dead skin cells because of the body’s inability to protect itself.
Additionally UVA rays are also found to contribute to premature aging. Because it is able to penetrate deeper into the skin, it weakens the collagen bonds holding the skin together. That results in weaker, less “plump” skin.
UVA rays was initially thought to be less damaging because it requires more time and exposure to progress into something concerning. However, there has been a lot of evidence to show that UVA rays does significant damage. Since 95% of UVA rays reach the earth and is able to penetrate through clouds and glass, we are always exposed to UVA rays. Thankfully, more sunscreen products are accounting to include UVA protection.
Below you can see a photo from a popular study by the New England Journal of Medicine on sun damage. The portrait of the 69-year truck driver captures the extent of sun damage that can occur from prolonged exposure without protection from UV rays.
Does sunlight treat my acne and acne scars?
As you can see sunlight can be quite troublesome for the health of our skin. For some of you, this may be old news. But for the many of us who grew up believing the sun is able to heal our acne or eczema, it may be counterintuitive.
So, here’s the question: does sunlight do anything for your acne?
The idea that sun light can heal your acne comes from an incomplete understanding of how our skin works. Sure, the sun may dry out your skin for a little bit reducing the oiliness our acne loves or give us a tan, making the acne we have look less pronounced. Additionally, the science is clear that UV rays do kill P. acnes bacteria that lead to acne inflammation. However, this is only half the story.
While in the beginning drying out your skin can seem necessary, the skin is a powerful barrier that helps you retain your moisture. By over-exposing yourself to sunlight, you damage your skin, causing it to shed oil and water. This makes the acne temporarily fade as it relies on these mechanisms to stay active. However, because it doesn’t remove the oil by speeding up the turnover cycle (like most acne treatments do) but rather by damaging the skin, your body responds by increasing oil production, leaving you with more acne. Also, as we learned earlier, UV rays are notable to penetrate very deep into the skin layer. So, if you have cystic acne which is lodged deeper into the skin, it will not work.
So, let’s not play with sunlight. Here are a few tips to protect you from harming your skin.
Even though, sunlight is not great for your skin, doesn’t mean that you should avoid it completely. There is much evidence to suggest that sunlight improves your mood, sleep quality, and mental health. You don’t have to deprive yourself from these benefits in the name of the skincare.
Just make sure to use sunscreen (and reapply), avoid overexposure, and try to get some sun in the morning. Morning sunlight is a little less harmful.
So, this begs the question: is light damaging for your skin?
The answer is no. The explanation is in the next chapter
How does LED light affects your skin?
There are a few lessons we can take away from this article so far. Two of the most important are wear your sunscreen, and light can definitely affect your skin. But not all lights are created equal. Unlike UV light, there are other lights that help than harm your skin, i.e. LED lights.
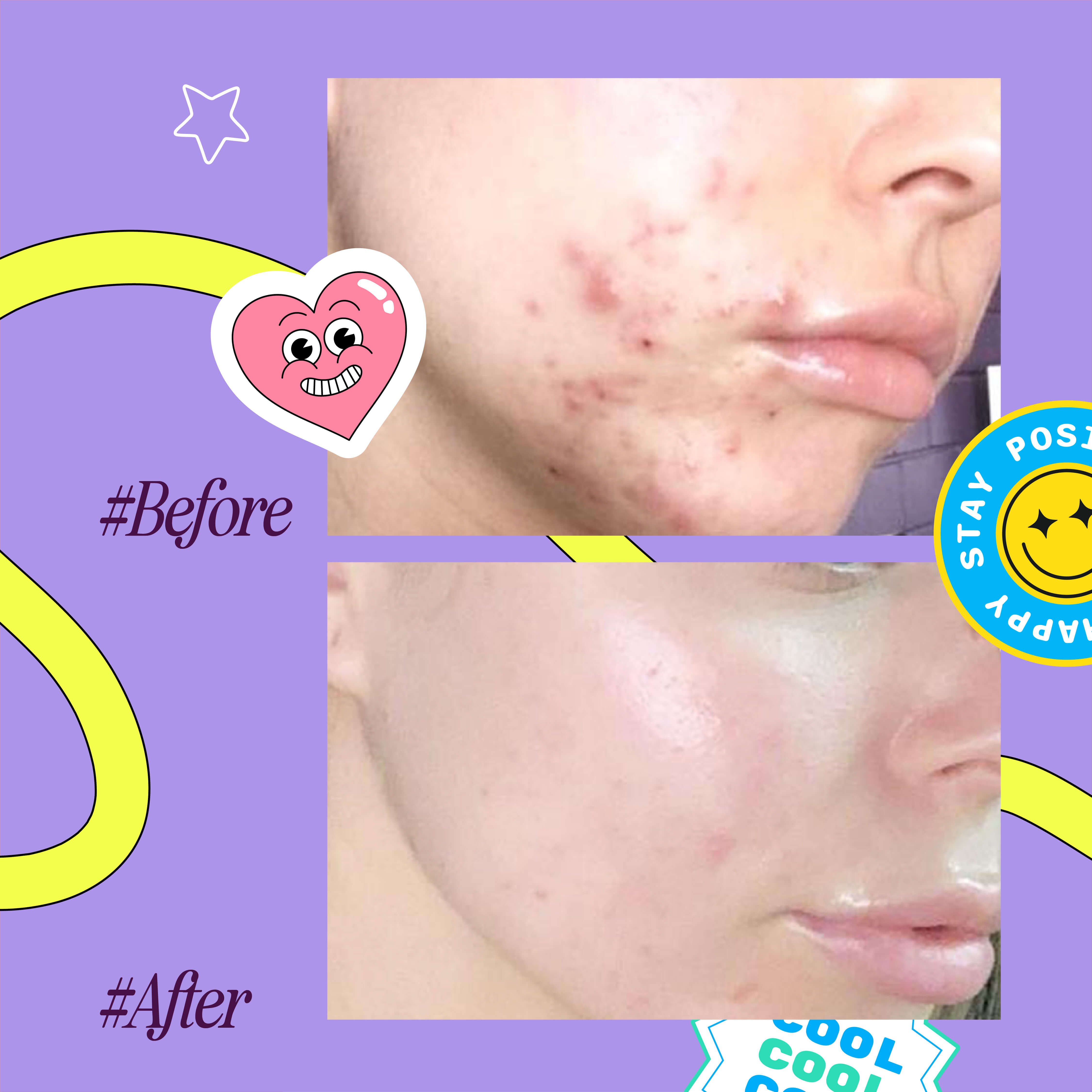
LED light is probably one of the best things you can do for your skin. And we are not just saying that. Even the origin story of LED light is already a testimony to why this light is beneficial. LED light therapy was first discovered by NASA scientists when they were looking into wound-healing treatments for astronauts in outer space. They found that red light, with enough exposure and consistency, was effective in doing so.
Since then, there has been a large body of research confirming that LED light is in fact useful in helping the body (and your skin) recover.
We’re not going to discuss all the several types of LED lights that can help your skin. However, we will discuss the two most evidence-backed LED light treatments: red and blue light.
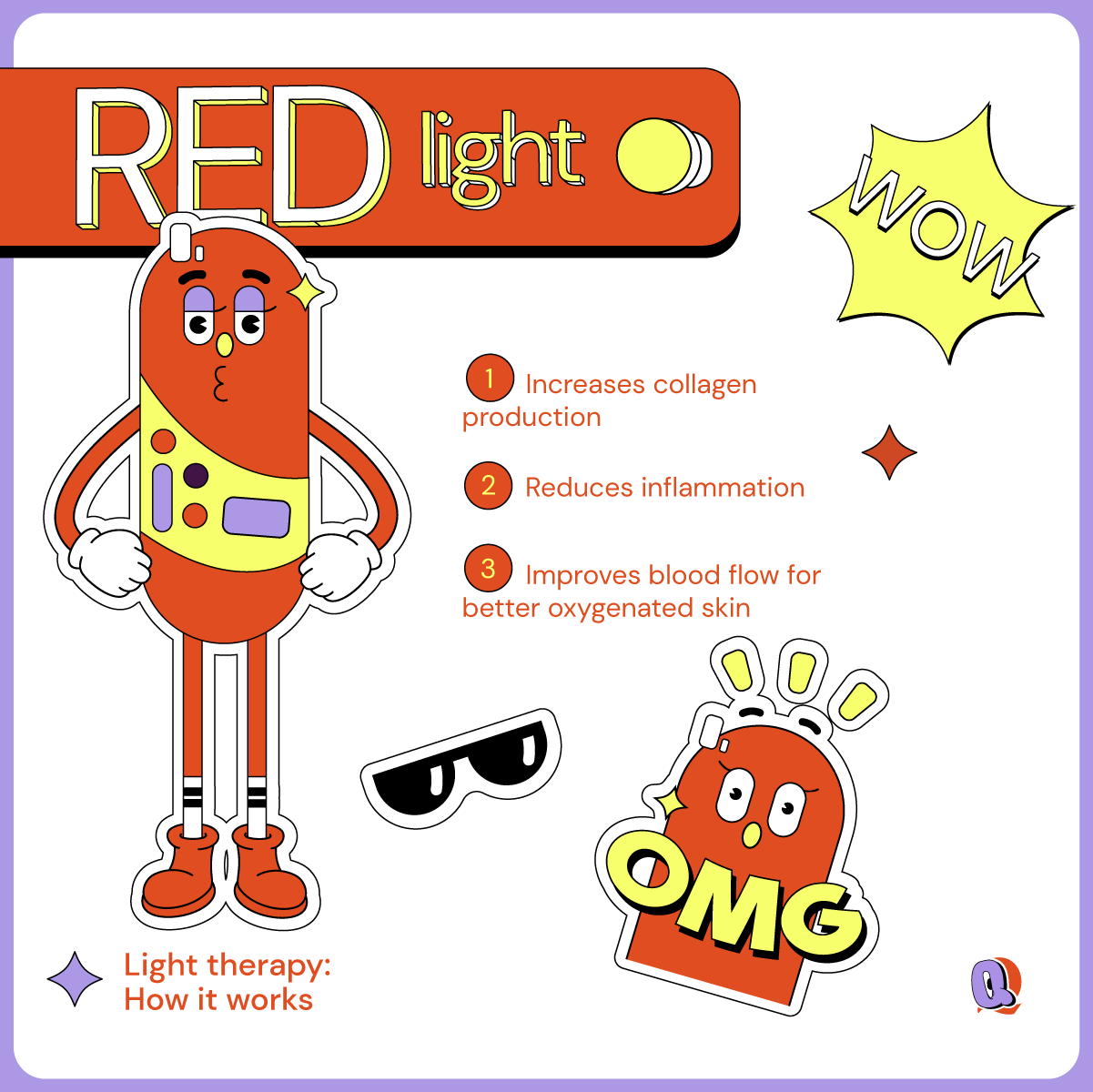
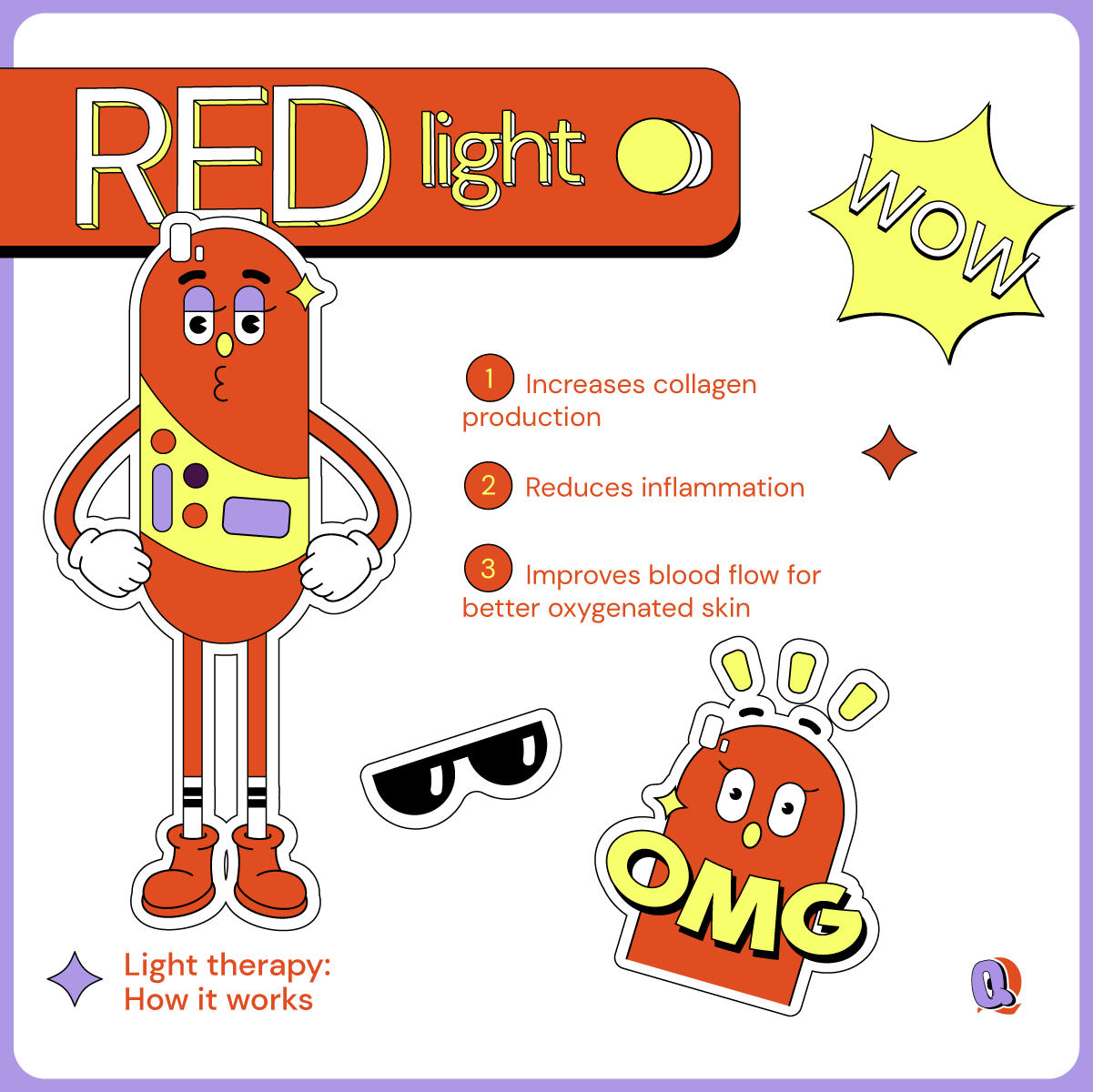
How does red light affect my skin?
Red LED light is in the heart of LED light therapy. It was the first to be discovered as a legitimate treatment for wounds and is widely trusted in the medical community.
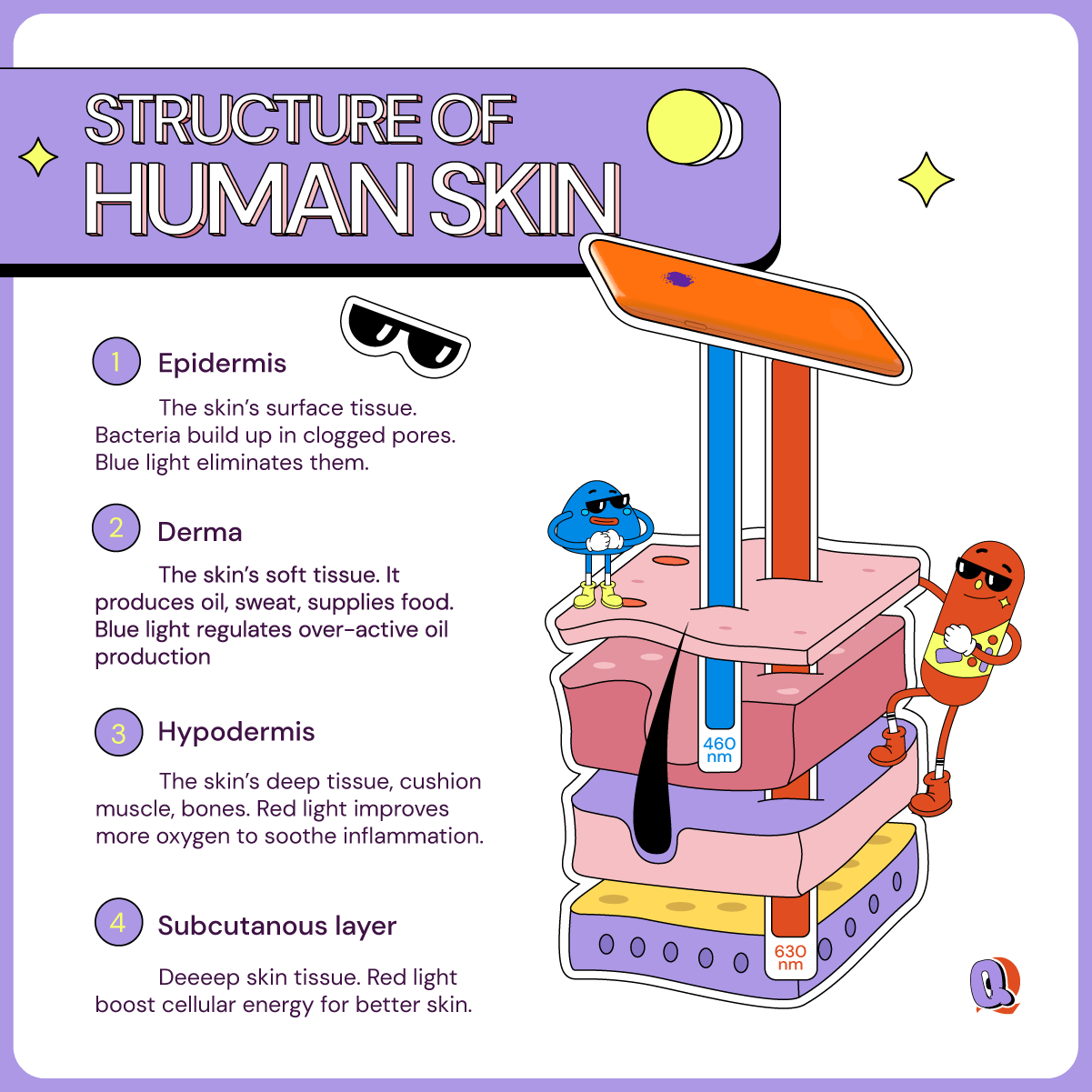
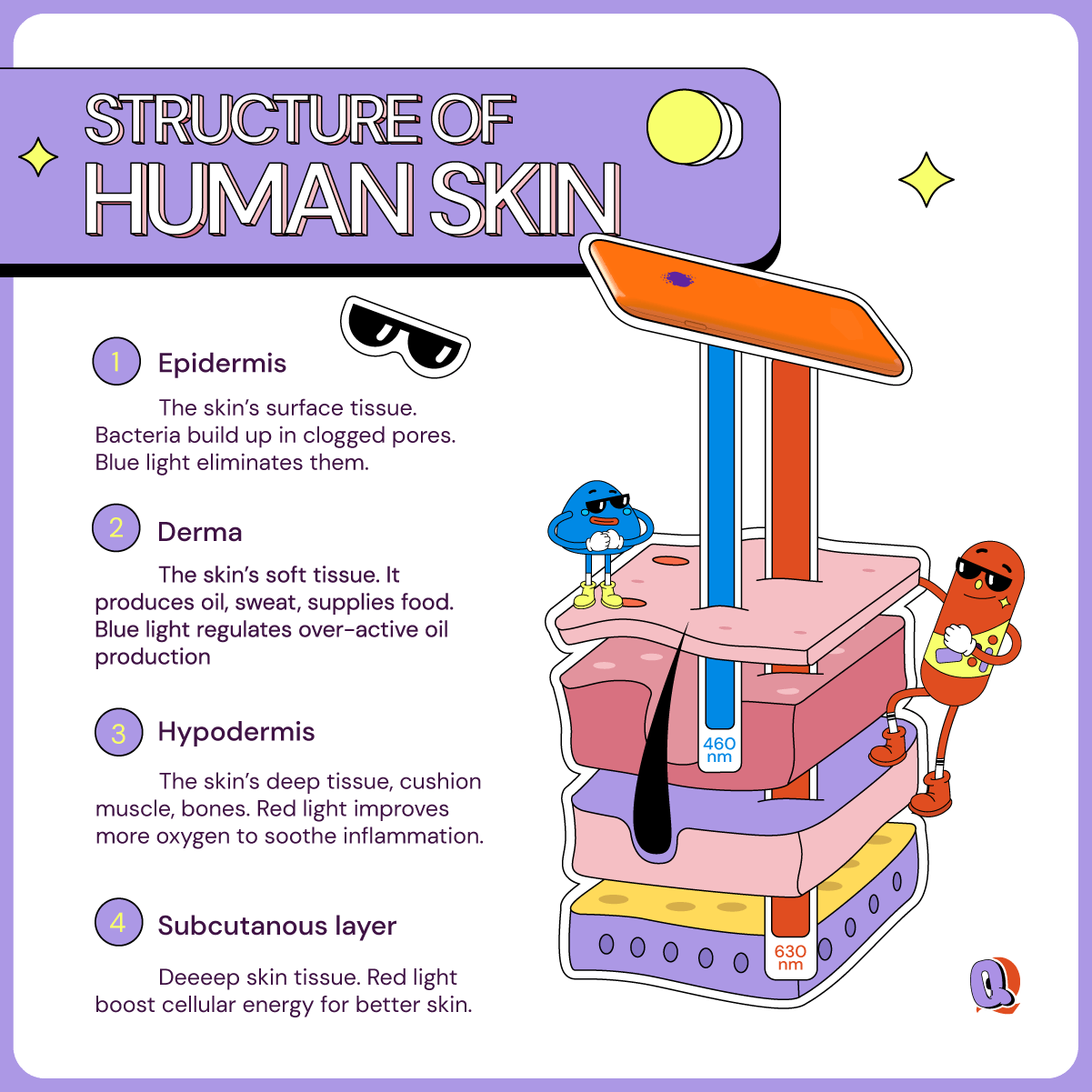
Red LED light has a wavelength between 600-650nm and so is able to penetrate much deeper into the skin than UV light. It can penetrate 1-2millimeters into the skin, all the way to hypodermis or subcutaneous layer. This means it can easily reach the dermis layer (above the hypodermis layer) where it is able to stimulate fibroblast cells to synthesize collagen and elastin proteins. It does this by tricking the skin into thinking that it is damaged without actually harming the skin at all. This “trick” triggers a wound-healing response, stimulating collagen production and therefore filling up textural gaps in the skin.
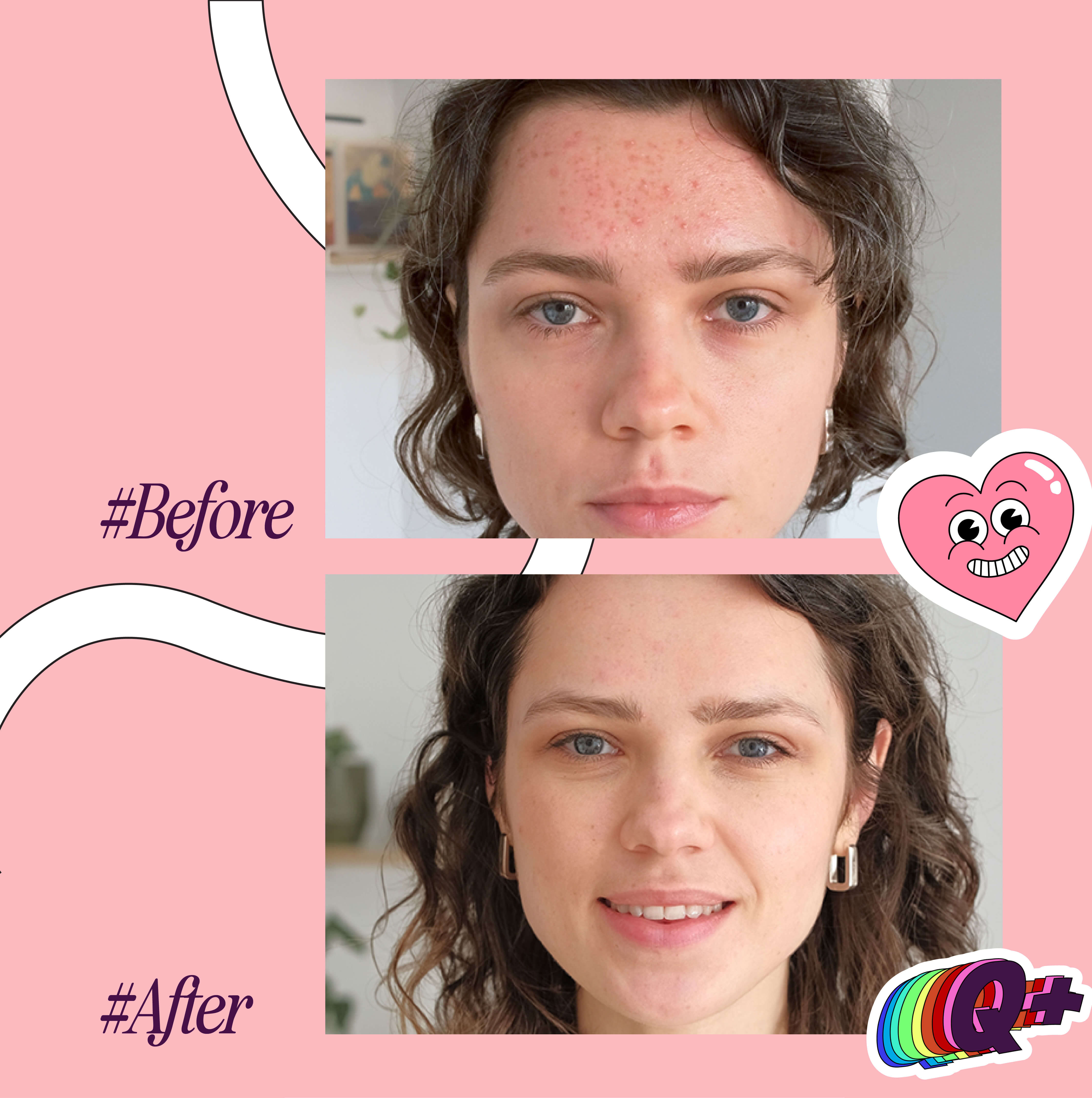
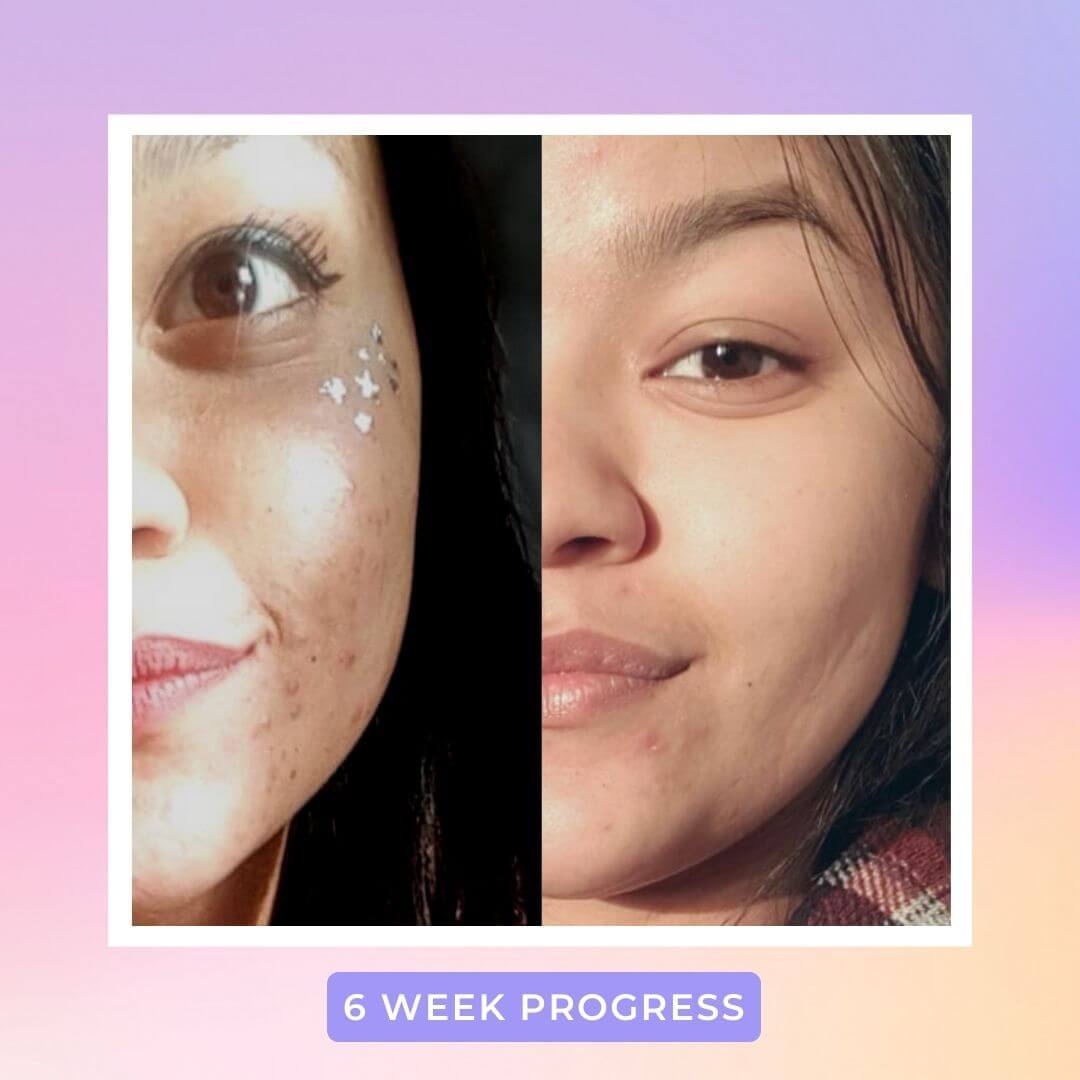
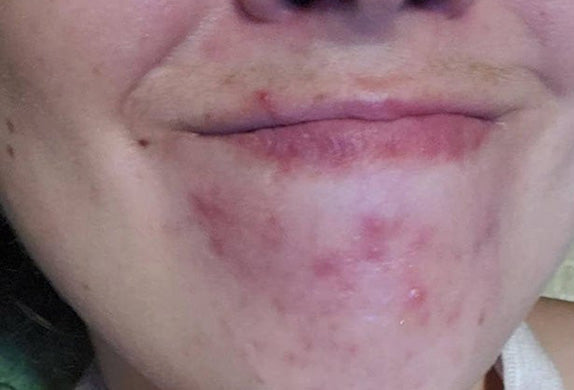
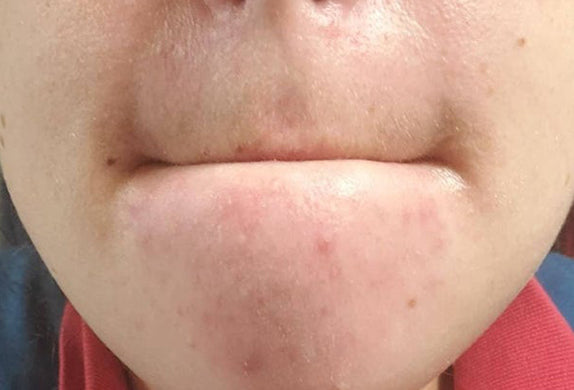
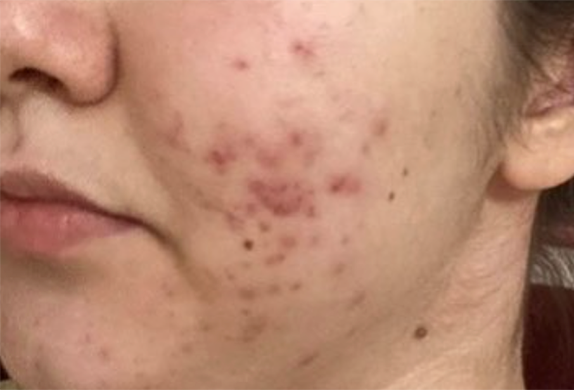
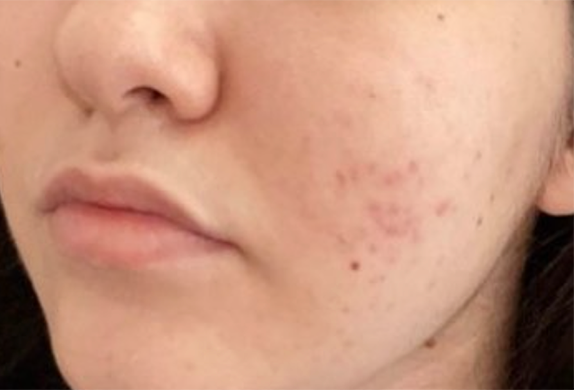
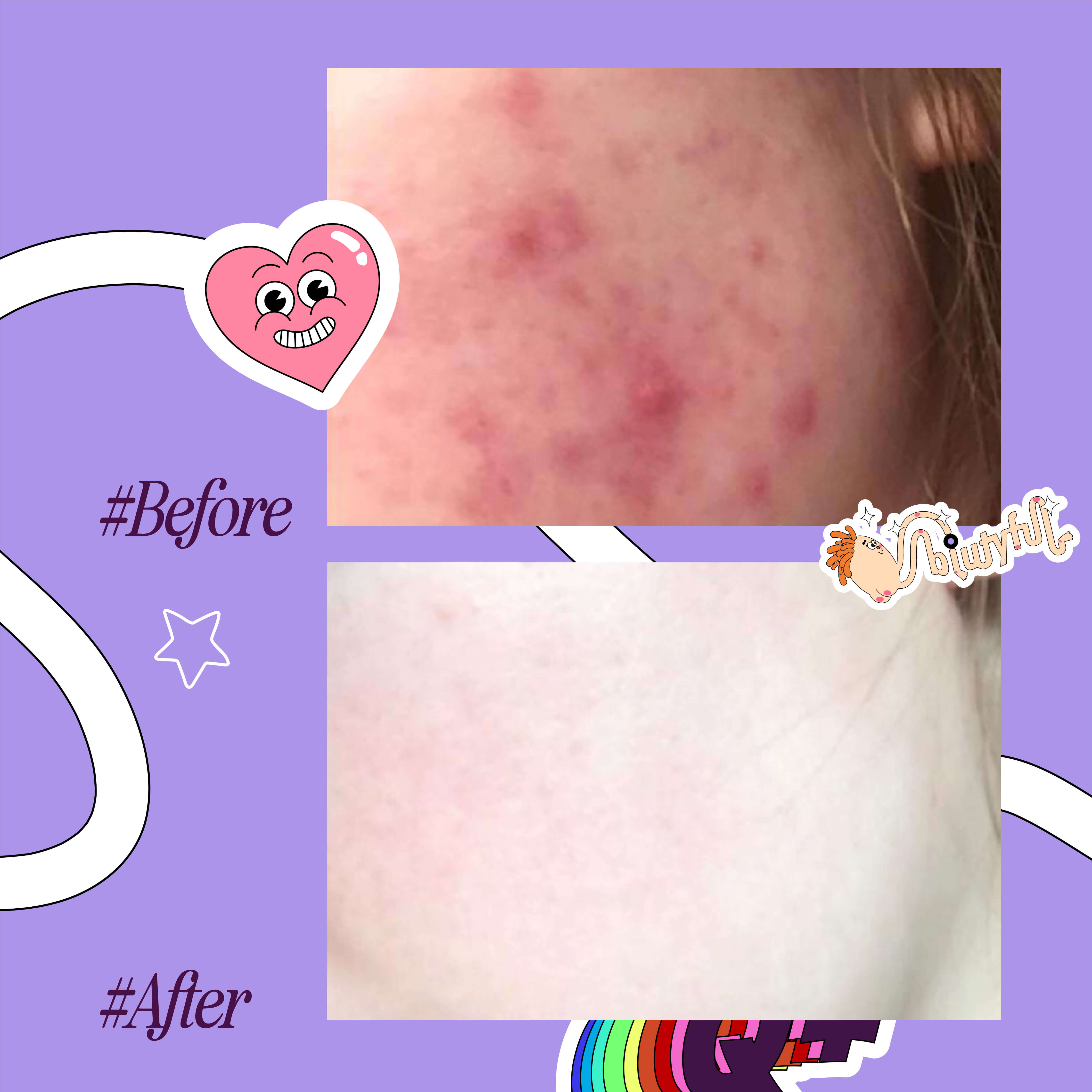
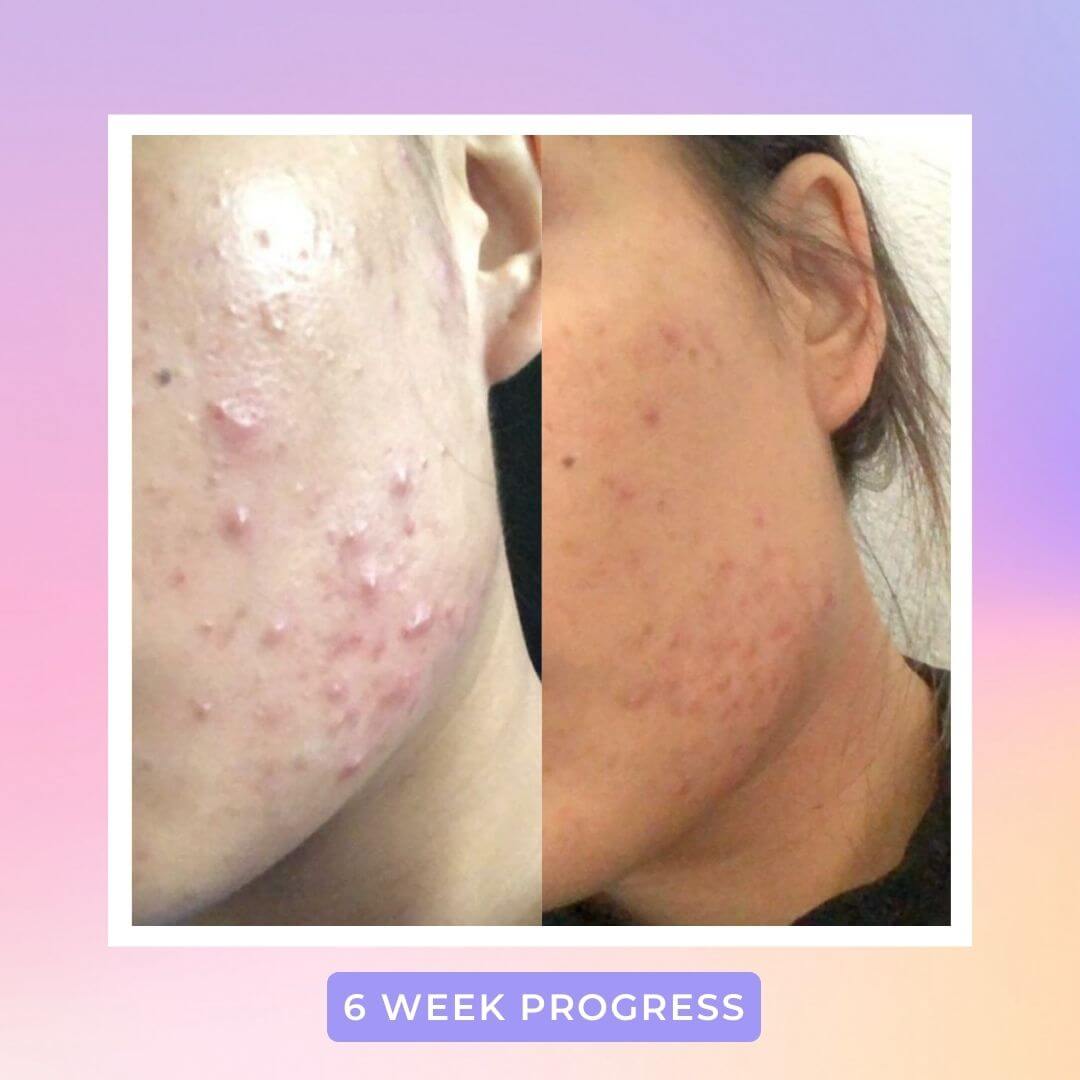
That’s why it’s red light therapy is so effective in healing textural inconsistencies like acne scars, fine lines, wrinkles and so on in the skin. Because red light is able to trigger a healing response, it also improves blood circulation to the targeted area which helps repair other forms common skin issues like calming inflammation or even reversing photodamage (a result of overexposure to the skin). Studies have also shown that red light helps repair the skin barrier, which means more moisture retention moving forward.
Of course, it’s not a magic pill. Red light therapy will not show immediate results. But with enough consistency (usually 6-12 weeks), you’ll start to notice healthier, smoother, and softer skin.
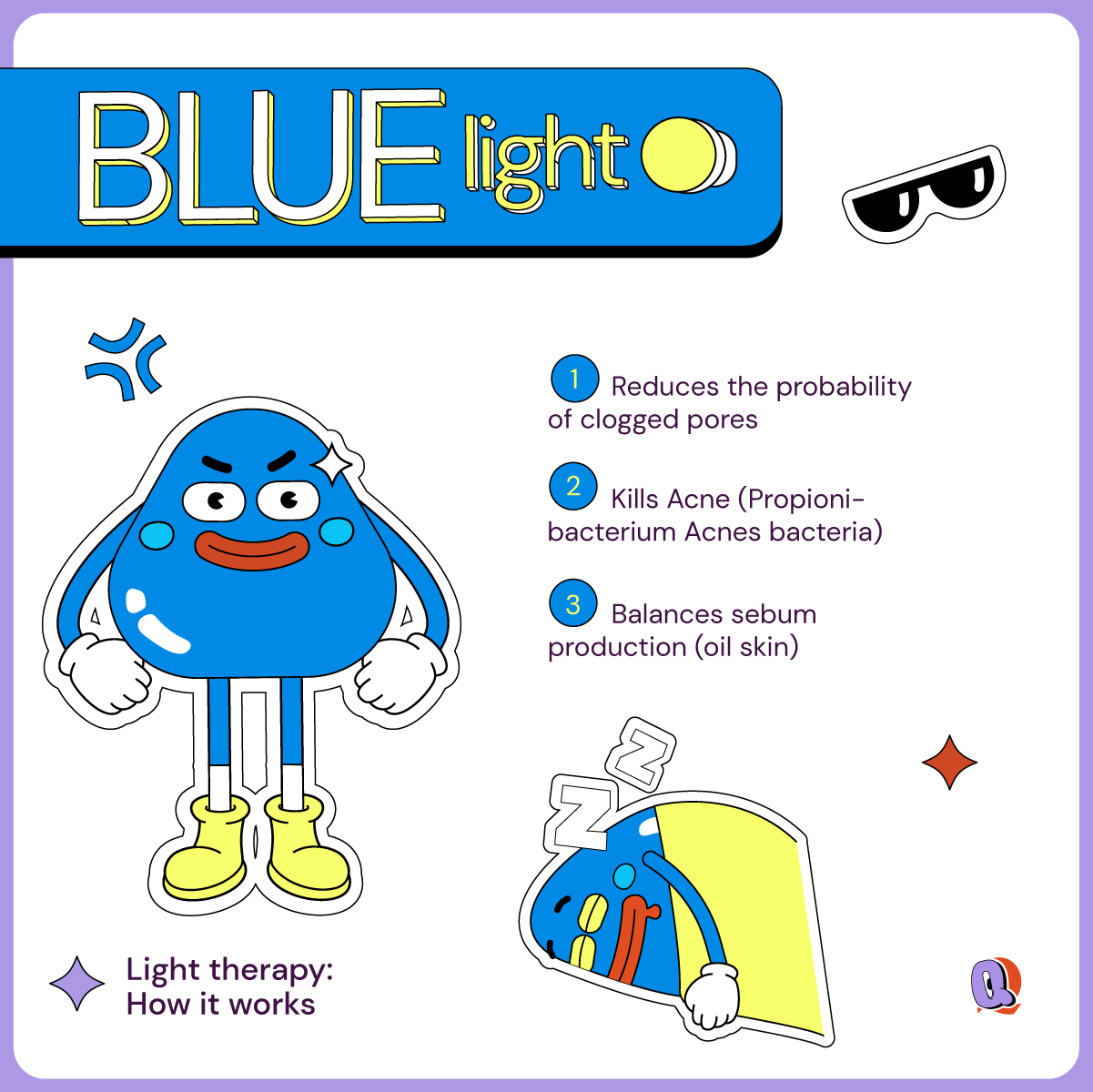
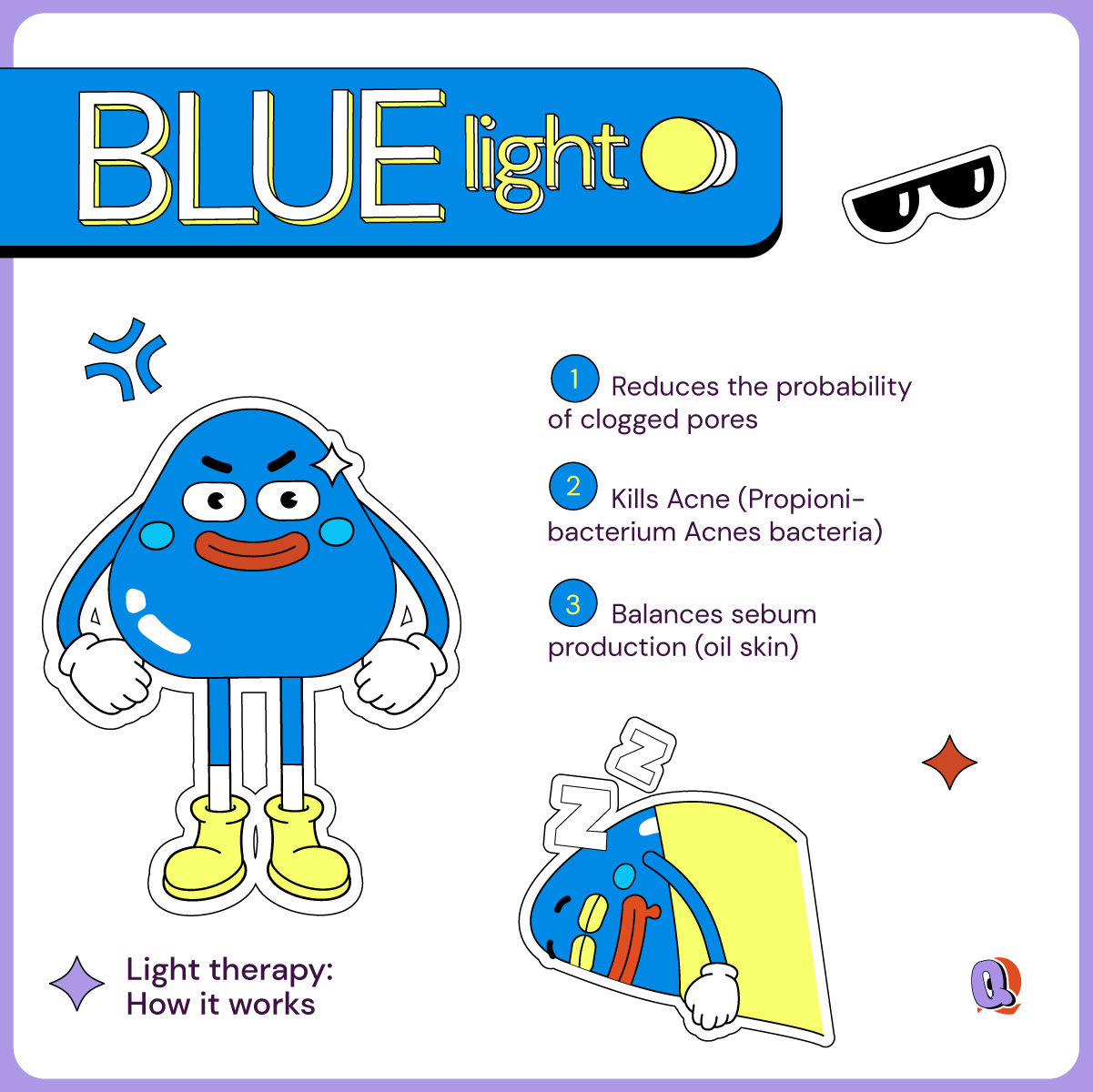
How does Blue light affect your skin?
Blue light is usually around the 415nm, sitting on the threshold between UV and visible light. So, it’s still got some fight in it. Since it has a much shorter wavelength than red light, it does not penetrate so deep into the skin, but works more on the surface of the skin. And it is a great solution to treat active pimples already present in the skin. It works kind of like a deep cleanse than a healing treatment like red light.
Blue light heals pimples in two ways: by regulating sebum and killing bacteria. Blue light works effectively in reducing sebum (usually caused by overactive hormones in teenagers). This reduces the possibility of clogged pores. This means it up to 60% reduction in comedonal lesions like white and black heads, 40% reduction in papular lesions, and 65%reduction in pustular lesions. Additionally, blue light has antimicrobial properties. This means it is lethal to a number of bacteria (including P. acnes bacteria) which causes inflamed pimples and other fungi (which causes fungal acne and other skin infections). Basically, it has all the benefits of UV light without the irreversible damage to the skin. By preventing the pimples from getting inflamed, blue light also effectively reduces the chances of getting deep scars when pimples do show up.
Another interesting side-benefit of blue light is that it increases serotonin- or your happy hormone. That means you feel better about the world and yourself. All in all, blue light is a winner when it comes to helping your skin.
The only thing to be cautious about when using blue light is to protect the eyes. While it may not be very dangerous if you accidently see blue light, overexposure can affect your vision. Luckily goggles are cheap and eyelids are free!